
High Hydrogen Storage in Trigonal Prismatic Monomer-Based Highly Porous Aromatic Frameworks
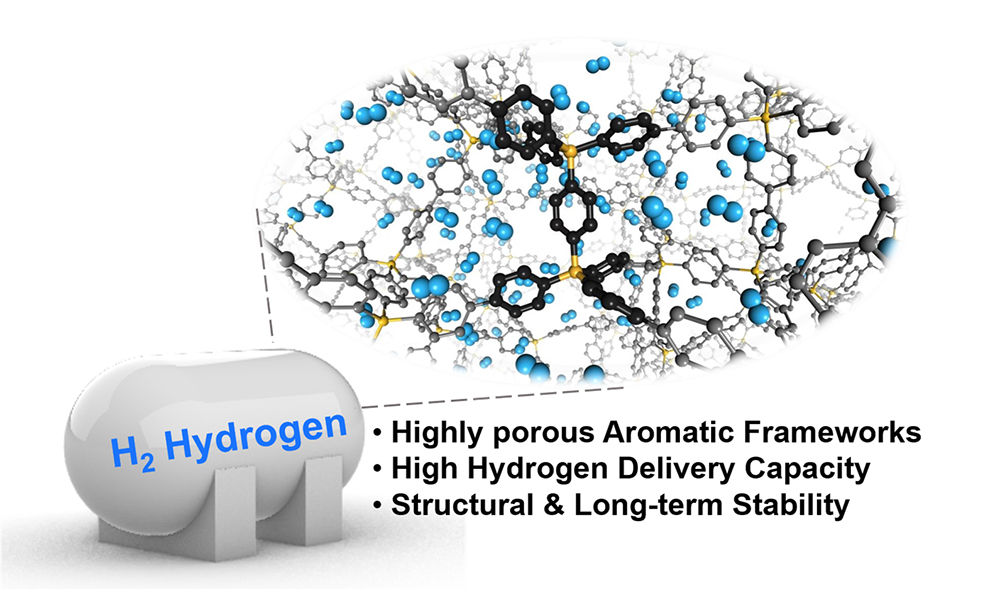
Hydrogen storage is crucial in the shift toward a carbon-neutral society, where hydrogen serves as a pivotal renewable energy source. Utilizing porous materials can provide an efficient hydrogen storage solution, reducing tank pressures to manageable levels and circumventing the energy-intensive and costly current technological infrastructure. Herein, two highly porous aromatic 𝖿rameworks (PAFs), C-PAF and Si-PAF, prepared through a Yamamoto C─C coupling reaction between trigonal prismatic monomers, are reported. These PAFs exhibit large pore volumes and Brunauer–Emmett–Teller areas, 3.93 ㎤/g-1 and 4857 ㎡/g-1 for C-PAF, and 3.80 ㎤/g-1 and 6099 ㎡/g-1 for Si-PAF, respectively. Si-PAF exhibits a record-high gravimetric hydrogen delivery capacity of 17.01 wt% and a superior volumetric capacity of 46.5 g L-1 under pressure-temperature swing adsorption conditions (77 K, 100 bar → 160 K,5 bar), outperforming benchmark hydrogen storage materials. By virtue of therobust C─C covalent bond, both PAFs show impressive structural stabilities in harsh environments and unprecedented long-term durability. Computational modeling methods are employed to simulate and investigate the structural and adsorption properties of the PAFs. These results demonstrate that C-PAF and Si-PAF are promising materials for efficient hydrogen storage.
* Reference
- Authors (Pusan National University, School of Chemical Engineering)
· Co-First author: Yu Chen
· Co-corresponding author: Prof. Yongchul G. Chung
- Title of original paper: High Hydrogen Storage in Trigonal Prismatic Monomer-Based Highly Porous Aromatic 𝖥rameworks
- Journal: Advanced Materials

 935정용철교수1.jpg
(299KB)
935정용철교수1.jpg
(299KB)